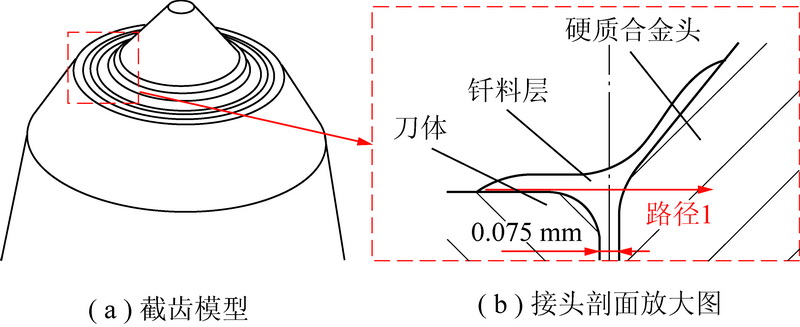
摘要:
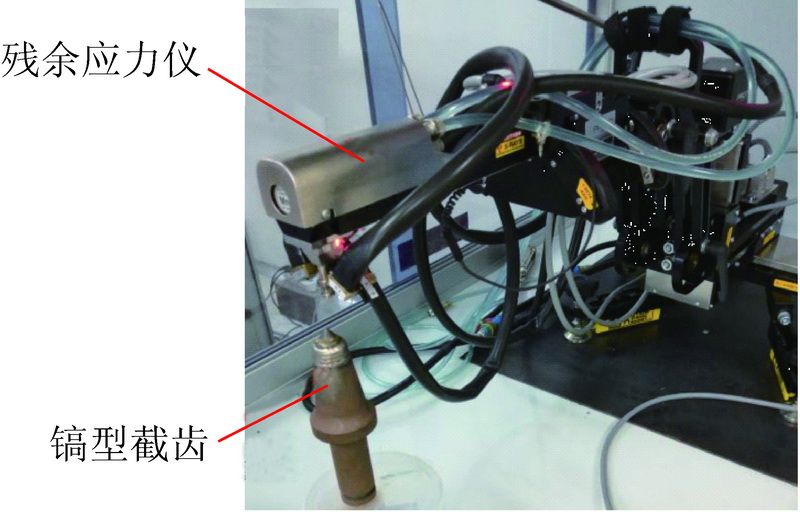
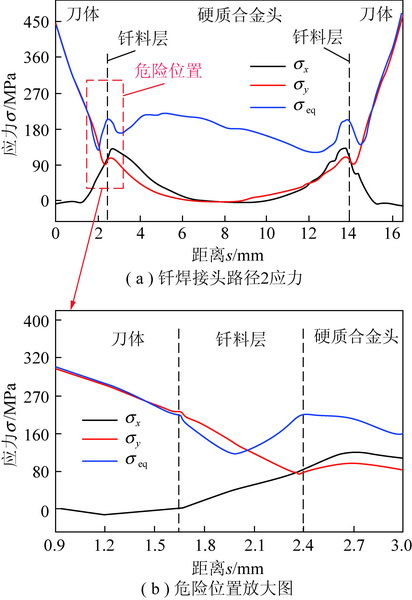
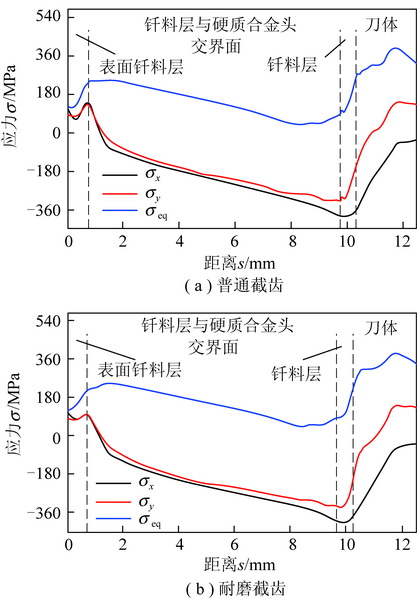
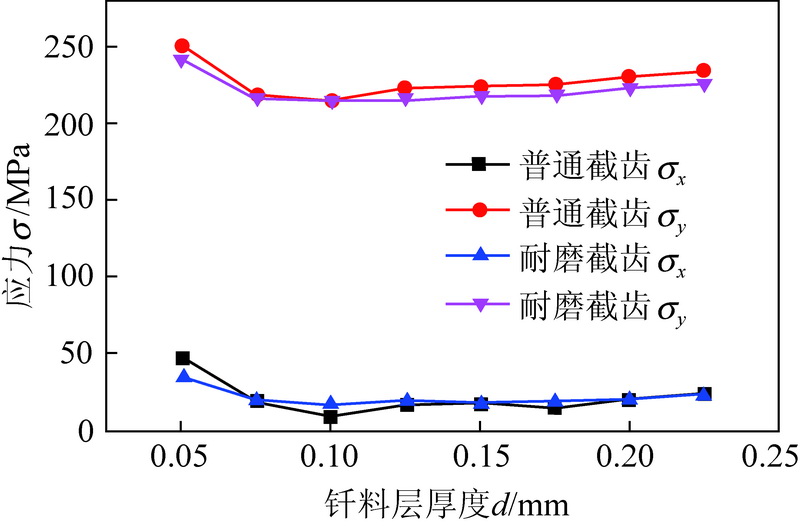
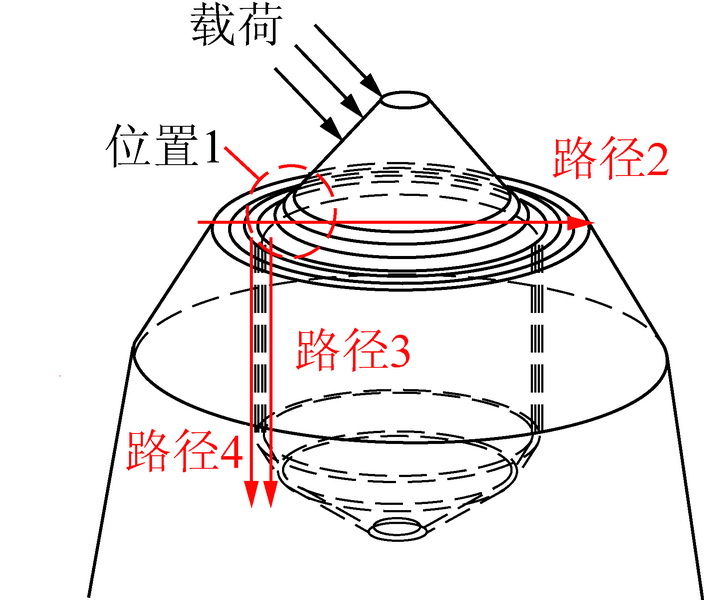
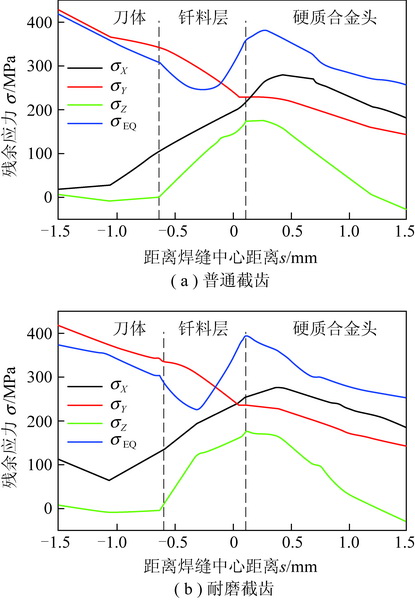
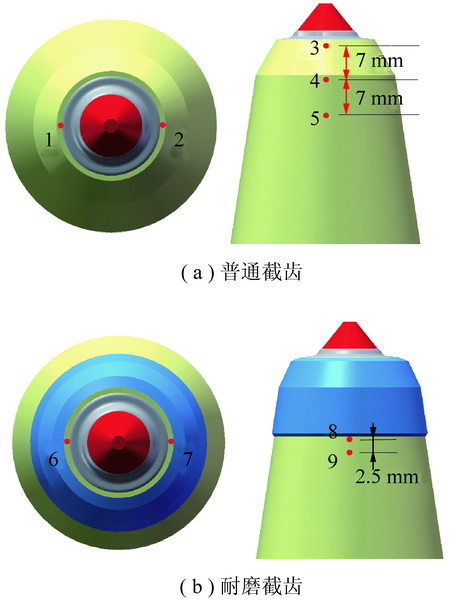
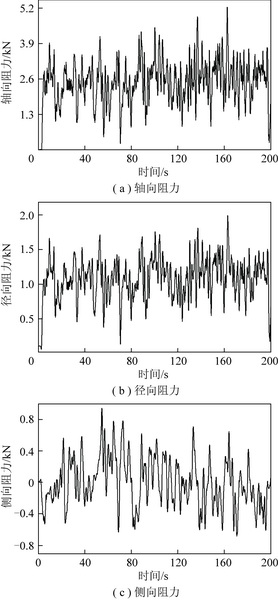
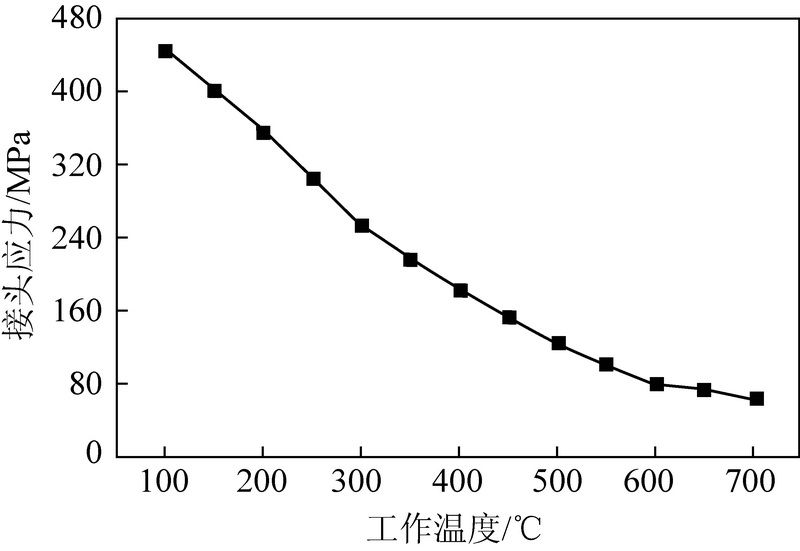
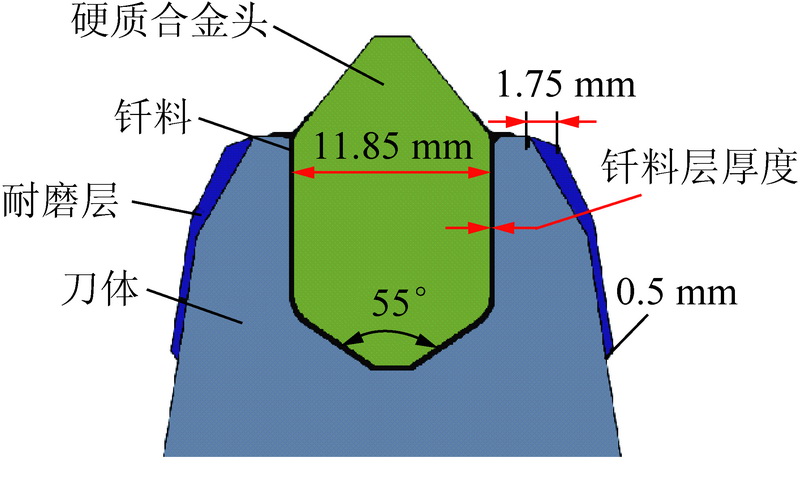
为了探究镐型截齿的硬质合金头脱落现象,针对普通截齿与耐磨截齿,研究镐型截齿工作 过程中的钎焊接头应力分布情况以及钎料层厚度对接头应力的影响特征。 利用 ANSYS 软件,分别 建立普通截齿与耐磨截齿的弹塑性热力学模型,对两种镐型截齿进行热-结构顺序耦合分析,得到 其钎焊残余应力分布,用实验验证模型正确性。 将截齿破岩时的工作温度及外部载荷施加到钎焊 残余应力模型上,仿真得到镐型截齿工作时钎焊接头的应力分布规律。 分析结果表明:① 未工作 状态下,两种镐型截齿的钎料层与硬质合金头交界面处均出现最大钎焊残余应力,容易发生因热应 力过大导致的钎缝开裂。 ② 工作状态下,截齿的径向路径上,普通截齿与耐磨截齿的钎焊接头应 力最大值近乎相等,均达到 210 MPa 左右,但其最大应力出现的位置不同,分别位于钎料层与刀体 的交界面以及钎料层与硬质合金头的交界面处;轴向路径上,两种镐型截齿的应力最大值相差不 大,且均出现在钎焊接头外表面处。 耐磨层对镐型截齿整体应力的分布影响不大,但却使得镐型截 齿最大应力出现的位置发生了偏移,使得镐型截齿硬质合金头脱落的危险位置发生变化。 ③ 普通 截齿与耐磨截齿均在钎料层厚度为 0.1 mm 时得到接头应力最小值,此时镐型截齿钎焊接头的连 接性能最好。
Abstract:
In order to investigate the cemented carbide head shedding phenomenon of picks,the stress distribution of brazed joints in pick working process and the influence of brazing filler thickness on the brazed joint stress were stud-ied. Using the ANSYS software,the elastic-plastic thermodynamic models of common pick and wear-resistant pick were established respectively. The thermal-structural sequential coupling analysis of the two picks were carried out to obtain the distribution of brazing residual stress,and the correctness of the models were verified by experiments. The working temperature and load of the pick were applied to the brazing residual stress model,and the stress distribution of the brazed joint was simulated. The results showed that ① under normal conditions,the maximum residual brazing stresses appeared at the interface between brazing filler and cemented carbide head of the two picks,which are prone to the cracking of the brazing seam caused by excessive thermal stress. ② Under working condition,the maximum stresses of brazed joints of common pick and wear-resistant pick were nearly equal in the radial path,reaching about 210 MPa, but the locations of the maximum stress were different. The maximum stress of common pick was located at the inter-face between brazing filler and pick body,while the maximum stress of wear-resistant pick was located at the interface between brazing filler and cemented carbide head. On the axial path,the maximum stresses of the two picks were not much different,and both of them appeared on the outer surface of brazed joint. Wear resistant layer has little effect on the overall stress distribution of pick,but it made the position of the maximum stress of pick shift and changes the dan-gerous position of cemented carbide head shedding. ③ Both common pick and wear-resistant pick have the minimum joint stress when the brazing filler thickness is 0. 1 mm,which makes the connection performance of brazed joints the best.
 百度学术
百度学术
 百度学术
百度学术
 本站查看
本站查看
 百度学术
百度学术




 下载:
下载: